Aim

tree supported high seat
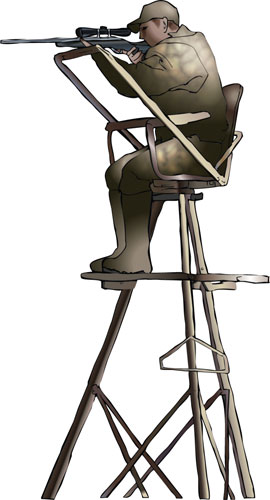
free-standing high seat
This guide provides information on types, siting and use of high seats and deer hides, commonly known as doe boxes.
Types of high seat
| Type | lean-to (including self-climbing high seats)‡ | free-standing | deer hide or doe box |
|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | Lean-to seats are set up against a structure such as a mature tree, and securely fastened by ropes or straps. Metal or wood. Can be either portable or permanent. | Stands alone supported on its own integral legs. Metal or wood. Usually permanent, may be semi-portable. | A fixed box or shooting platform/rail. More easily blends into the surrounding forest area making it visually unobtrusive. Permanent. Easy and safe to access. |
| Location | Often used on the edge of mature woodland or in glades, where a suitable tree is available. | Best used in areas where there is no support for a lean-to, to ensure the optimum vantage point. | Best situated on a vantage point overlooking the control area. |
| Disadvantages | Use limited to where a suitable, stable support can be found. The supporting tree may sway in high winds. The type most vulnerable to theft. | Must be secure as a structure and requires a stable, firm, level base. Not so easily moved. | Restricted to suitable vantage points. Not so easily moved. |
| Cost | Less expensive to purchase or construct than free standing seats. | More expensive than the lean-to design. | Relatively cheap to construct. |
Background
High seats are useful for
- Flat areas where either sighting of deer or provision of a safe backstop is is difficult or in habitats where stalking on foot is not effective.
- Protection of a vulnerable crop. A high seat will allow control of deer at a given location, particularly in agricultural or forestry land uses, where deer are:
• only using properties as a crossing point or are not resident,
• elusive or
• in habitats where stalking on foot is not effective. - Providing a fixed area over which to shoot safely.
Portable versus permanent
- The advantages of a portable aluminium/steel high seats are:
• they can be dismantled for transportation;
• they can be erected by a single person;
• a number of sites can be covered in a season;
• potential sites for permanent structures can be trialled for suitability.
- Where control is envisaged over an extended period, a permanent type should be considered.
Siting
Investigate all opportunities to use the topography of the ground to provide an elevated position before deciding to erect a high seat or hide. If a high seat is to be used, the following should be considered when deciding where to site it:
- Planning permission is not required if high seat is associated with forestry or agricultural protection. However, check with relevant planning department before erecting.
- Safety: locate away from known routes of public access where possible.
- Areas of frequent deer use/movement: utilise areas such as favourite feed areas and entry routes.
- Topography of the ground: use to conceal the high seat and occupant. Avoid siting on sky-lines. Also, high visibility may draw unwelcome attention to the seat.
- Prevailing wind: high seats should be approached into the prevailing wind. In forest situations consider brashing and clearing a route over the last 50 metres to allow a silent approach.
- Central location: In large control areas locate high seats centrally to enable a 360 degree arc of fire, provided it is safe to do so.
- Cover: use natural or artificial cover to help disguise any movement of the occupant.

a deer hide or "doe box"
Use
- Ensure that an appropriate risk assessment has been carried out and recorded where appropriate*
- Follow Health and Safety Executive (HSE) guidance and ensure that activities adhere to the relevant Health & Safety Legislation1**
- Ensure the high seat is safe and fit-for-purpose before use and has not been tampered with. Ensure that high seats are continually maintained.
- Ensure a minimum of three points of contact on the ladder, between hands and feet when climbing.
- When two people are using a double high seat only one person should climb or descend the ladder at a time.
- Ensure that there are no rounds in the chamber of the firearm (ie status A,B or C ***) when climbing up and down the high seat.
- When two people are using a double high seat ensure that the status of all firearms present has been checked and confirmed between parties at all stages.
- Only chamber a round once stable in the seat.
- Never assume that because you are in a high seat that there are safe backdrops for all shots***.
- Be aware of the dangers of falling asleep and hypothermia.
- If using a dog, ensure that it is secured safely below the highseat but not attached to it.
- Identify range markers to inform of shooting distances.
Maintenance
- Carry out a formal inspection annually and record results. Carry out any maintenance work necessary before use.
- Construct wooden ladders from a strong straight grained wood i.e. Larch. Construct with rungs checked into the uprights as well as fi xed with screws. Staple round fence wire and small mesh wire across the rung, to provide extra strength and sure footing in wet conditions.
- Do not paint the ladder as this may cover up cracks in the wood.
- When constructing a floor area ensure that boards are heavy enough to take the desired weight and are fully supported by cross supports. Treated timber is best for load-bearing timbers.
- Fasten lean-to seats securely to the support, by either ropes or a ratchet belt. In situations where vandalism is likely also secure with a chain and padlock.
- Remove old seats no longer in use or decaying.
- Numbering high seats and recording their position may aid future location. Recording high seat number in larder records may also help inform future management.
Preventing unauthorised access
- Install a ladder shroud or remove the lower section of ladder to prevent unauthorised use.
- Fix a sign to the ladder stating “Warning: No unauthorised use”.
- Where possible site the high seat away from view of the casual walker.
1. Work at height Regulations 2005. Legislation available online at www.opsi.gov.uk or can be obtained from the Stationary Office.
Further useful information: HSE’s Falls from height website: www.hse.gov.uk. Information can also be obtained from HSE Books.
For addresses and contact details see BPG Useful Contacts
